Introduction
In today’s digital-first business landscape, organizations generate and consume massive amounts of data and documents every day. Managing this content effectively is critical for efficiency, compliance, and collaboration. That’s where Enterprise Content Management (ECM) comes in. But what exactly is ECM, and why is it so important for modern enterprises? In this comprehensive beginner’s guide, we’ll explore what ECM is, its core components, key benefits, use cases, and how businesses can successfully implement an ECM system.
Definition
Enterprise Content Management (ECM) is a system of strategies, tools, and technologies used to capture, manage, store, preserve, and deliver content and documents related to organizational processes. Its goal is to streamline access to information, improve workflow efficiency, ensure regulatory compliance, and support decision-making by organizing both structured and unstructured data across the enterprise.
What Is Enterprise Content Management?
Enterprise Content Management (ECM) refers to the strategies, tools, and technologies used to capture, manage, store, preserve, and deliver content and documents related to business processes. ECM helps organizations handle unstructured data – like emails, contracts, invoices, and reports – throughout its entire lifecycle.
Whether it’s a scanned paper document, an email attachment, or a digital form, ECM ensures that the right people can access the right content at the right time – while maintaining security, compliance, and version control.
Core Components of ECM
An effective ECM system is composed of several integrated components, each playing a vital role in the content lifecycle:
Content Capture:
This involves the digitization and collection of content from various sources. Capture technologies include:
- Scanners for paper documents
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Email import tools
- Integration with third-party applications
Content Management:
Once captured, content must be organized and categorized. This includes:
- Metadata tagging
- Indexing
- Version control
- Folder structures and file hierarchies
Storage:
ECM provides a secure, centralized repository for storing documents and files. Storage solutions ensure that content is protected, redundant, and scalable.
Workflow and Process Automation:
Modern ECM systems support workflow automation, allowing for faster approvals, routing, and task management. For example, an invoice can automatically be routed to the finance department for approval.
Security and Compliance:
With built-in access controls, encryption, and audit trails, ECM ensures that sensitive content is protected and compliant with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX.
Search and Retrieval:
Advanced search capabilities allow users to quickly find relevant documents using keywords, metadata, or full-text search. This saves time and improves productivity.
Retention and Records Management:
ECM systems allow organizations to manage the lifecycle of records, ensuring that documents are archived or deleted based on legal and regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Enterprise Content Management
Implementing an ECM system offers numerous benefits across departments and industries:
Improved Productivity:
By centralizing information and enabling quick retrieval, ECM reduces the time employees spend searching for documents and allows them to focus on core tasks.
Enhanced Collaboration:
Teams can collaborate in real-time on shared content, track revisions, and maintain document integrity, even across multiple locations.
Cost Savings:
Reducing paper usage, storage space, and manual processes translates into significant cost reductions over time.
Regulatory Compliance:
ECM helps organizations comply with industry standards and legal requirements by enforcing document retention policies and audit trails.
Data Security:
Granular user permissions, encryption, and monitoring tools ensure that sensitive information remains secure from unauthorized access or data breaches.
Disaster Recovery:
A robust ECM system provides reliable backups and ensures business continuity in case of disasters like hardware failure, fire, or cyberattacks.
Common Use Cases for ECM
1. Human Resources
- Storing employee records
- Automating onboarding/offboarding processes
- Managing benefits documentation
2. Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing and approvals
- Expense report management
- Auditing and compliance
3. Legal
- Contract management
- Case file tracking
- Document version control and collaboration
4. Healthcare
- Patient record management
- Compliance with HIPAA regulations
- Streamlining insurance and billing processes
5. Government and Public Sector
- Handling permits, licenses, and citizen services
- Maintaining transparency and audit readiness
- Archiving public records
ECM vs. Document Management System (DMS)
While often used interchangeably, ECM is broader than a traditional Document Management System (DMS). A DMS focuses primarily on storing and organizing documents. In contrast, ECM encompasses document management plus workflow automation, compliance, and records management across the enterprise.
On-Premises vs. Cloud-Based ECM
Modern ECM platforms are available in both on-premises and cloud-based models:
- On-Premises ECM: Installed and managed on local servers. Offers greater control but requires significant IT resources.
- Cloud ECM: Hosted in the cloud, offering scalability, remote access, and lower upfront costs. Popular platforms include Microsoft SharePoint, OpenText, M-Files, and Box.
How to Implement an ECM System
Successfully implementing ECM requires strategic planning and cross-functional collaboration. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
Assess Needs:
Understand what types of content your organization handles and what challenges you’re trying to solve (e.g., compliance, slow approvals, or scattered documents).
Get Stakeholder Buy-In:
Involve departments like IT, legal, HR, and finance early in the planning process. Their input ensures the ECM solution meets real-world needs.
Choose the Right Platform:
Evaluate ECM vendors based on features, scalability, integration capabilities, and user-friendliness. Consider whether a cloud or hybrid deployment is best.
Develop a Governance Strategy:
Set clear policies for content classification, access control, retention, and compliance. Train employees on how to use the system responsibly.
Migrate Content:
Digitize and migrate existing paper and digital files into the new system. Use metadata and indexing to maintain structure and searchability.
Roll Out in Phases:
Avoid overwhelming users by deploying the system in stages, starting with a pilot group. Gather feedback and refine the system accordingly.
Monitor and Optimize:
Track usage, performance, and compliance regularly. Make adjustments to workflows, permissions, or training as needed.
Future of Enterprise Content Management
As digital transformation accelerates, ECM is evolving to incorporate technologies like:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) for content classification and analytics
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate repetitive tasks
- Machine Learning to improve search relevance and data extraction
- Mobile Access to empower remote and field employees
- Integration with Collaboration Tools like Microsoft Teams and Slack
These innovations promise to make ECM even more intelligent, seamless, and user-friendly in the coming years.
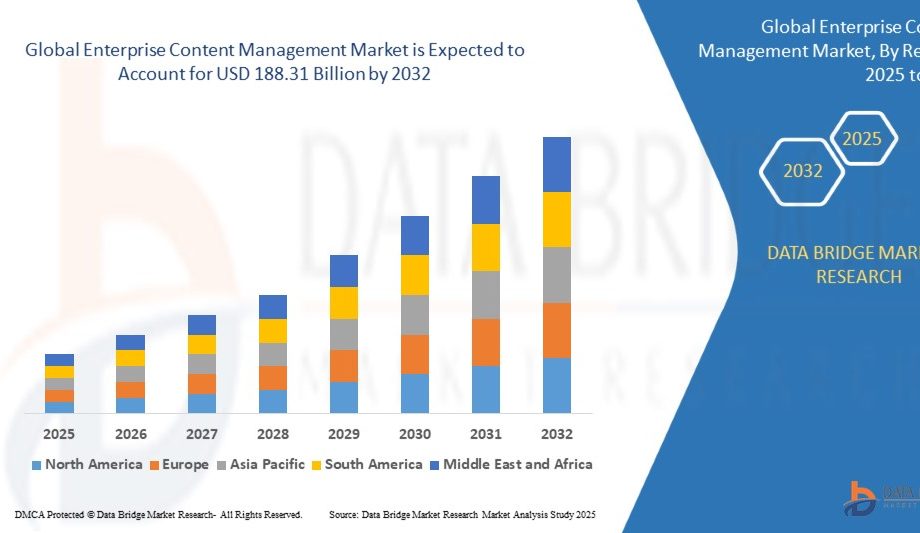
Growth Rate of Enterprise Content Management Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the worldwide enterprise content management market was estimated at USD 66.02 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.1% to reach USD 188.31 billion by 2032.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-enterprise-content-management-market
Conclusion
Enterprise Content Management is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for businesses looking to remain competitive, compliant, and efficient in the digital age. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, implementing an ECM system can streamline operations, reduce costs, and unlock new opportunities for collaboration and innovation.

 :
: