Wart Removal is a common skin concern that can appear unexpectedly and cause both physical discomfort and emotional distress. These small, grainy skin growths are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and can appear anywhere on the body, most commonly on the hands, feet, and face. While generally harmless, warts are contagious and may multiply or spread if left untreated.
This comprehensive guide explores the types of warts, treatment options, home remedies, and tips for prevention to help you achieve and maintain clearer skin.
What is Wart Removal?
Wart Removal are benign (non-cancerous) skin growths caused by certain strains of HPV. The virus triggers rapid growth of keratin, a hard protein on the skin’s surface. Warts vary in appearance depending on their type and location, but they typically feel rough to the touch and may have black dots in the center (clotted blood vessels).
Common Types of Warts:
Common Warts (Verruca vulgaris)
Usually found on fingers, knuckles, and elbows, these are rough and dome-shaped.
Plantar Warts
Found on the soles of the feet, plantar warts can be painful due to pressure from walking. They often grow inward.
Flat Warts
These are smoother and smaller, often appearing on the face, neck, or legs. They may occur in large numbers.
Filiform Warts
Long and thread-like, these typically grow on the face, especially around the eyes, nose, and mouth.
Periungual Warts
Found around or under the fingernails and toenails, these can be painful and disrupt nail growth.
Causes and Risk Factors
HPV spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact or indirectly via surfaces like shower floors or shared razors. You’re more likely to get warts if:
Your immune system is weakened
You have cuts or abrasions on your skin
You frequently walk barefoot in communal areas
You bite your nails or pick at your skin
Children and teens are particularly susceptible due to their more active lifestyles and developing immune systems.
When to See a Doctor
While many Wart Removal are harmless and go away on their own over time, you should seek medical attention if:
The wart is painful, bleeding, or changing in appearance
You have multiple warts spreading rapidly
The wart doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments
You have diabetes or a weakened immune system
The wart is on your face or genital area
Treatment Options for Wart Removal
There is no guaranteed cure for warts, and treatments aim to remove the wart or stimulate the immune system to fight the virus. Some warts may require multiple sessions or combined therapies.
1. Over-the-Counter Treatments
Salicylic Acid: This common ingredient peels away the infected skin gradually. It’s available as drops, gels, and patches. Consistency is key—daily application for several weeks is usually needed.
Freezing Sprays: These contain dimethyl ether and propane to freeze the wart. While not as strong as professional cryotherapy, they can work on small warts with repeated use.
2. Prescription Treatments
Stronger Salicylic Acid Formulations: These may be prescribed for stubborn warts.
Imiquimod (Aldara): A cream that boosts the body’s immune response to HPV.
Cantharidin: Applied by a healthcare professional, it causes a blister to form under the wart, lifting it off.
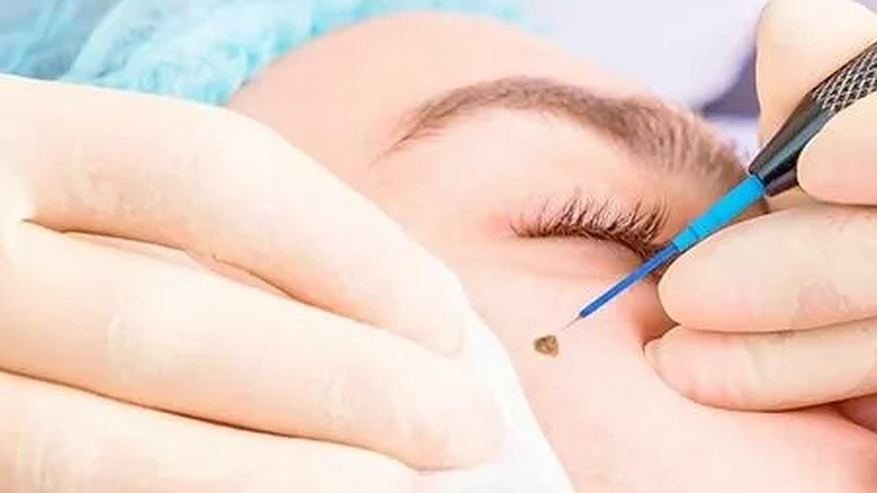
3. Professional Wart Removal Methods
Cryotherapy: Freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. This is more potent than OTC sprays and may require several sessions.
Laser Treatment: Pulsed-dye lasers target blood vessels feeding the wart, causing it to die and fall off.
Electrosurgery and Curettage: Burning the wart with an electric current and scraping it off.
Surgical Excision: Physically cutting out the wart, typically used for large or resistant warts.
Natural and Home Remedies
While scientific evidence is limited, some people find relief using natural remedies:
Duct Tape Occlusion Therapy: Covering the wart with duct tape for several days, soaking and scrubbing, and repeating the cycle.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Thought to work like salicylic acid. Apply with a cotton ball and cover overnight.
Garlic: Known for antiviral properties. Crushed garlic is applied to the wart and covered.
Banana Peel: The inside contains enzymes that may help dissolve the wart.
Note: Natural remedies may not be effective for everyone and can irritate. Discontinue if the skin becomes overly sore or inflamed.
Wart Prevention Tips
Because warts are contagious, preventing their spread is essential:
Don’t pick or scratch at warts
Wash your hands regularly
Keep feet dry and wear flip-flops in public showers
Avoid sharing towels, socks, or razors
Cover warts with bandages to prevent the spread
Boost your immune system with a healthy diet, sleep, and regular exercise
For those with recurrent or stubborn warts, HPV vaccination (like Gardasil) may offer some benefit by protecting against strains that cause genital warts and possibly others.
Dealing with Genital Warts
Genital warts are a separate condition caused by different strains of HPV. These require specific medical evaluation and treatment. They are sexually transmitted and may need prescription medications, cryotherapy, or other procedures. Practicing safe sex and getting the HPV vaccine can help prevent transmission.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Though warts are medically minor, they can have a significant psychological toll, especially when visible on the face or hands. Children and teens may experience bullying or embarrassment. Seeking treatment not only improves the skin but can also boost self-esteem and confidence.
Conclusion
Warts are a common skin condition, but with the right knowledge and approach, they can be effectively treated and prevented. Whether you choose over-the-counter options, professional treatments, or home remedies, persistence and patience are key. If you’re unsure about a skin growth or if treatments don’t seem to work, consult a dermatologist for expert care.
Clearer skin is within reach—with the right strategy, you can say goodbye to warts and hello to renewed confidence.
 :
https://www.pinterest.com/
:
https://www.pinterest.com/